Wireshark
Wireshark, the most powerful packet sniffer and protocol analyser can be used to sniff data out of the captured packets for various protocols.
Network communication takes place in packets and any request like http get/post is broken down into multiple packets and then transmitted to the remote webserver.
Wireshark has the ability to reconstruct a communication stream using separate packets to show the actual conversation that took place.
This feature can be used to easily view the communication in plain text format, without having to read individual packets.
When used in combination with man in the middle attack/arp spoofing, this feature can be handy to sniff various http post data or the data submitted in forms. In this post I am going to show you how easy it is with wireshark.
Filter out html packets
The first thing to do is to start capturing packets on a interface with wireshark. And then do some http form submissions. Wireshark displays a column for the "Protocol". For http packets the column would show the value "HTTP".
Now lets filter out the http packets out of all other packets. This is very simple, just type http in the filter box and hit enter. Wireshark would right away remove all non-http packets out of view.
But this is not enough. We need to see those specific packets that initiated an http GET or POST request. To do this, filter further with the following expression
http.request
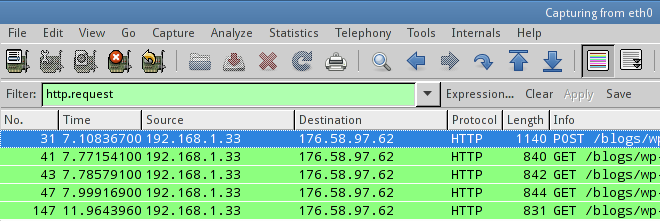
If you wish to see only the POST request packets, use the following filter
http.request.method=="POST"
So now wireshark shows those packets that initiate an http request. But remember these packets do no have the full data. So to view the full request data, right click a packet and click "Follow TCP Stream".
It will open up a dialog that shows the full http request by combining all the packets of the particular tcp stream (sequence).
Notes
Now if the form submission takes place over https (SSL) then wireshark won't be able to show anything, since the data in the packet would be encrypted.
The encryption takes place right in the browser and then the encrypted data is transmitted through the packets over the network.
If you prefer the console then there is a program called tshark that can be used for the same task. It is the console version of wireshark.