Multipass is a tool used to generate cloud-style Ubuntu VMs quickly on Linux, macOS, and Windows. It's designed for developers who want a fresh Ubuntu environment with a single command. It uses KVM on Linux, Hyper-V on Windows, and HyperKit on macOS to run the VM with minimal overhead.
The tool gives you a simple but powerful CLI that allows you to access an Ubuntu command line quickly or create your own local mini-cloud.
It can also be used for Local development and testing, which is otherwise a pain. Multipass makes it easier by automating all of your setup and teardown. It has a growing library of images that give you the ability to launch purpose-built VMs or custom VMs you've configured yourself through its powerful cloud-init interface.
Developers can use Multipass to prototype cloud deployments and to create fresh, customized Linux dev environments on any machine. Mac and Windows users can use Multipass as the quickest way to get an Ubuntu command line on their system. New Ubuntu users can use it as a sandbox to try new things without affecting their host machine and without the need to dual boot.
Installation
As mentioned, Multipass uses Hyper-V or VirtualBox on Windows as Virtualization providers. It employs Hyper-V by default to launch Virtual Machines. But in some devices, it is not enabled by default, which makes Hyper-V option grey out on installation.
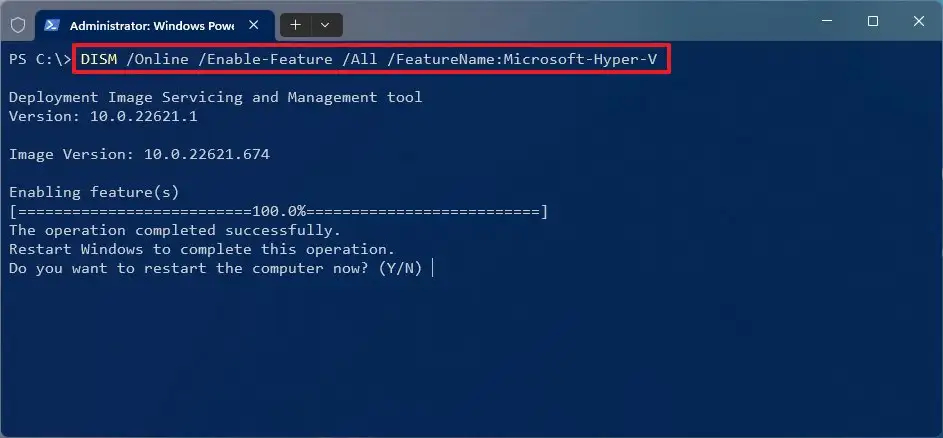
To enable Hyper-V, turn on Virtualization on BIOS Settings and open Power Shell as Administrator. Then, run the following command:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V
You can download VirtualBox from the official providers. The useful links and resources are provided at the end.
Download the Multipass installer from the link given in Links and Resources. Run the installer and go with the on-screen instructions. You can select Hyper-V if it's supported on your PC or Install VirtualBox.
Creating an Ubuntu Instance
GUI Simple Method
Launch Multipass by searching for it in the search bar. You will see a pop-up notification for Multipass. In the Hidden Icons menu, you will find the Multipass icon. Right-click on it and select Open Shell.
This method launches an instance of the latest version of Ubuntu with the instance name of primary.
You can see the following output on the terminal:
Launched: primary Skipping mount due to disabled mounts feature Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.15.0-73-generic x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage System information as of Tue Jun 6 01:20:08 UTC 2023 System load: 1.111328125 Processes: 95 Usage of /: 30.3% of 4.67GB Users logged in: 0 Memory usage: 20% IPv4 address for enp0s3: 10.0.2.15 Swap usage: 0% Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled. 0 updates can be applied immediately. Enable ESM Apps to receive additional future security updates. See https://ubuntu.com/esm or run: sudo pro status To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>". See "man sudo_root" for details. ubuntu@primary:~$
Let's test it out!
As we just learned, the previous step automatically mounted our $HOME directory in the instance. Let's try out a few more Linux commands to see what we're working with:
ubuntu@primary:~$ free
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 976420 176480 445352 964 354588 661152
Swap: 0 0 0
ubuntu@primary:~$ df
.Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
tmpfs 97644 960 96684 1% /run
/dev/sda1 4893836 1519828 3357624 32% /
tmpfs 488208 0 488208 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5120 0 5120 0% /run/lock
/dev/sda15 106858 6182 100677 6% /boot/efi
tmpfs 97640 4 97636 1% /run/user/1000
Congratulations, you've got your first instance!
This instance is great for when we just need a quick Ubuntu VM, but let's say we want a more customized instance. Multipass has us covered there too!
Manual Command Line Method
Open the Windows Terminal and run the following command:
PS C:\Users> multipass find
Image Aliases Version Description core core16 20200818 Ubuntu Core 16 core18 20211124 Ubuntu Core 18 core20 20230119 Ubuntu Core 20 core22 20230119 Ubuntu Core 22 snapcraft:core18 18.04 20201111 Snapcraft builder for Core 18 snapcraft:core20 20.04 20210921 Snapcraft builder for Core 20 snapcraft:core22 22.04 20220426 Snapcraft builder for Core 22 20.04 focal 20230530 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS 22.04 jammy,lts 20230602 Ubuntu 22.04 LTS 22.10 kinetic 20230530 Ubuntu 22.10 appliance:adguard-home 20200812 Ubuntu AdGuard Home Appliance appliance:mosquitto 20200812 Ubuntu Mosquitto Appliance appliance:nextcloud 20200812 Ubuntu Nextcloud Appliance appliance:openhab 20200812 Ubuntu openHAB Home Appliance appliance:plexmediaserver 20200812 Ubuntu Plex Media Server Appliance anbox-cloud-appliance latest Anbox Cloud Appliance charm-dev latest A development and testing environment for charmers docker 0.4 A Docker environment with Portainer and related tools jellyfin latest Jellyfin is a Free Software Media System that puts you in control of managing and streaming your media. minikube latest minikube is local Kubernetes ros-noetic 0.1 A development and testing environment for ROS Noetic. ros2-humble 0.1 A development and testing environment for ROS 2 Humble.
Let's launch an instance running Ubuntu 22.10 ("Jellyfin") by typing the following command:
PS C:\Users> multipass launch jellyfin Launched: jellyfin
You can check some basic information about your new instance with the below command:
PS C:\Users> multipass exec jellyfin -- lsb_release -a
This tells Multipass to execute the command lsb_release -a on the "jellyfin" instance.
No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Ubuntu Description: Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS Release: 22.04 Codename: jammy
Get a list of instances you have created by running the below command:
Multipass list
Name State IPv4 Image primary Running N/A Ubuntu 22.04 LTS expectant-pigeon Running N/A Ubuntu 22.10 jellyfin Running N/A Ubuntu 22.04 LTS primed-koel Running N/A Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
You can also stop and delete the running instances using the following commands:
Multipass stop primary
Multipass delete primary
PS C:\Users> multipass list Name State IPv4 Image primary Deleted -- Not Available expectant-pigeon Deleted -- Not Available jellyfin Running N/A Ubuntu 22.04 LTS primed-koel Deleted -- Not Available
Creating a Custom Instance
Custom Instances can be created with the precondition of specific disk space, memory, and CPU. Basically, there is an allocation of a specific amount of resources to the instance you are creating. With Multipass, you can allocate resources in the command line at the time of instance creation by running the below command.
PS C:\Users> multipass launch lts --name ltsInstance --memory 2G --disk 10G --cpus 2 Launched: ltsInstance
Now let's confirm if this new instance has the specs you're looking for with the following command:
PS C:\Users> multipass info ltsInstance Name: ltsInstance State: Running IPv4: N/A Release: Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS Image hash: 7d830df583e8 (Ubuntu 22.04 LTS) CPU(s): 2 Load: 0.08 0.05 0.06 Disk usage: 1.4GiB out of 9.5GiB Memory usage: 174.9MiB out of 1.9GiB Mounts: --
We can also run commands, upgrade the distro, and install packages like Apache web server, net-tools, PHP, etc., on created instances from the terminal, without opening the instance shell.
To do so, open the Terminal and type the following command:
PS C:\Users> multipass exec jellyfin sudo apt update Hit:1 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease Hit:2 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates InRelease Hit:3 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease Hit:4 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease Hit:5 https://repo.jellyfin.org/ubuntu jammy InRelease Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done 4 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.
This way we can run commands on created instances from the terminal without accessing the shell by launching it.
Installing Apache
Let's install Apache on VM from the terminal. Type the following command:
Multipass exec jellyfin sudo apt install apache2
It will install Apache on the VM instance. Let us check the web server status.
PS C:\Users> multipass exec jellyfin sudo systemctl status apache2
● apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2023-06-09 18:07:43 IST; 31s ago
Docs: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
Main PID: 3612 (apache2)
Tasks: 55 (limit: 4642)
Memory: 5.0M
CPU: 31ms
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
├─3612 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
├─3613 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
└─3614 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
Jun 09 18:07:43 jellyfin systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
Jun 09 18:07:43 jellyfin apachectl[3611]: AH00558: apache2: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified d>
Jun 09 18:07:43 jellyfin systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
As confirmed by this output, the service has started successfully.
Installing PHP
To install PHP, run the following command on the terminal:
Multipass exec jellyfin sudo apt install php
This allows you to install packages through the terminal, with the Multipass exec command on instances that are running.
Transferring files between an instance and the Host (Windows)
We can also transfer files between the host and the instance using the Multipass transfer command.
For example, to copy a local file (local_file.txt) to the default home folder of the instance jellyfin, run:
multipass transfer local_file.txt jellyfin:
In the same way, to copy a file (instance_file.txt) from the default home folder of the ample-pigeon instance to the current working folder, run:
multipass transfer ample-pigeon:remote_file.txt
Executing Commands Inside the Multipass VM Shell
Launch the Multipass shell that is running by executing the following command in the Terminal.
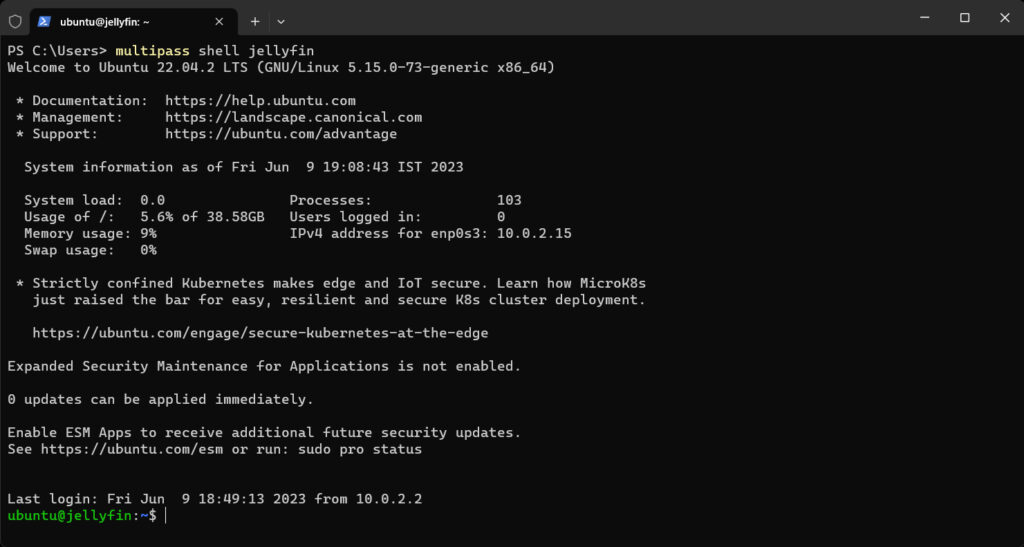
Multipass shell jellyfin
This command launches the jellyfin instance shell inside the terminal.
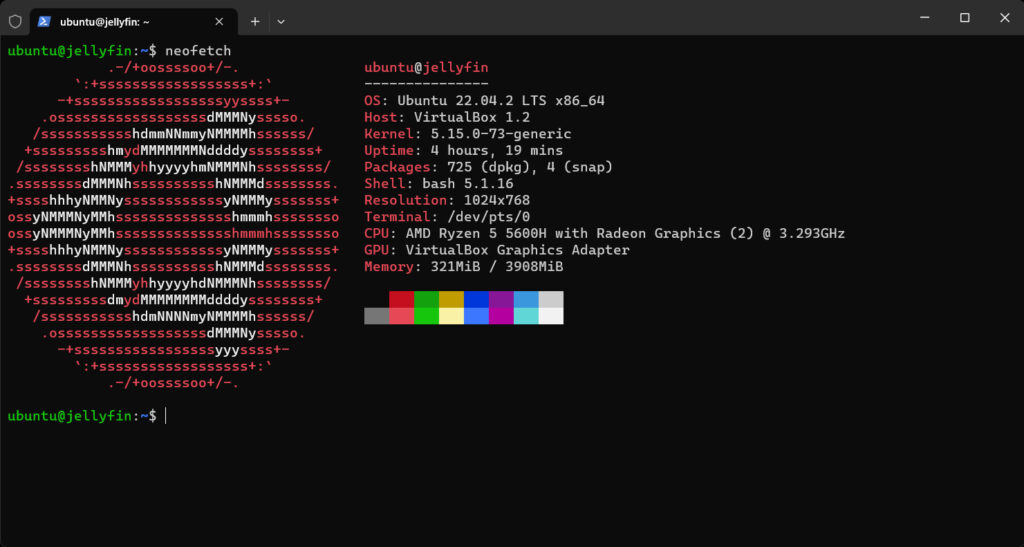
Let us now install neofetch package in the instance, and get system information from it.
sudo apt install neofetch
Neofetch
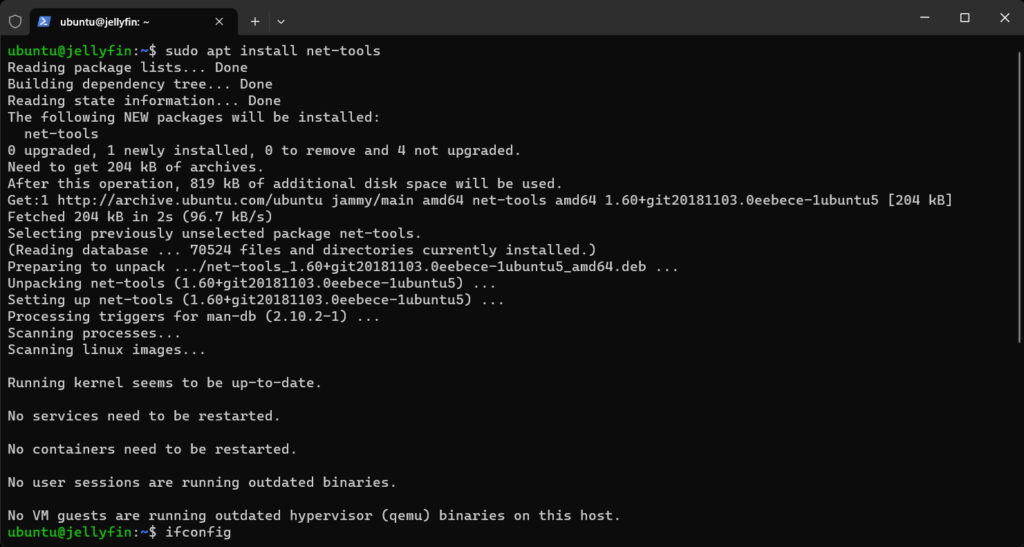
Installing net-tools
Sudo apt install net-tools
Checking Network Configuration
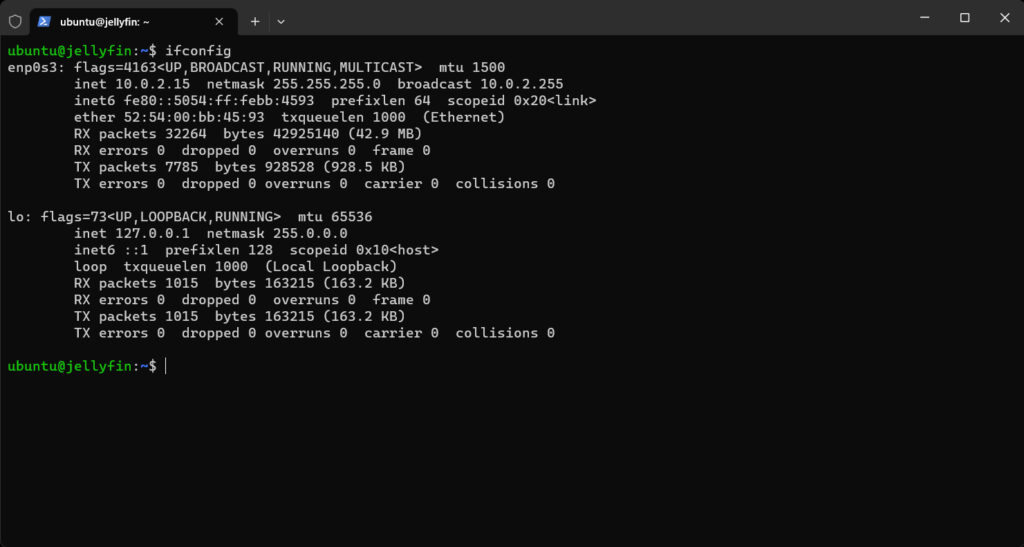
Let us check the Network Configuration of the instance using ifconfig.
Ifconfig
Configuring a new storage location
Open an administrator privileged PowerShell prompt and execute the following commands, replacing
PS> Stop-Service Multipass PS> Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment" -Name MULTIPASS_STORAGE -Value "<path>" PS> Start-Service Multipass
Links and Resources:
- Multipass Download Link: https://multipass.run/download/windows
- VirtualBox Download Link: https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/virtualbox/downloads/index.html